Visible Light IDentification
Introduction
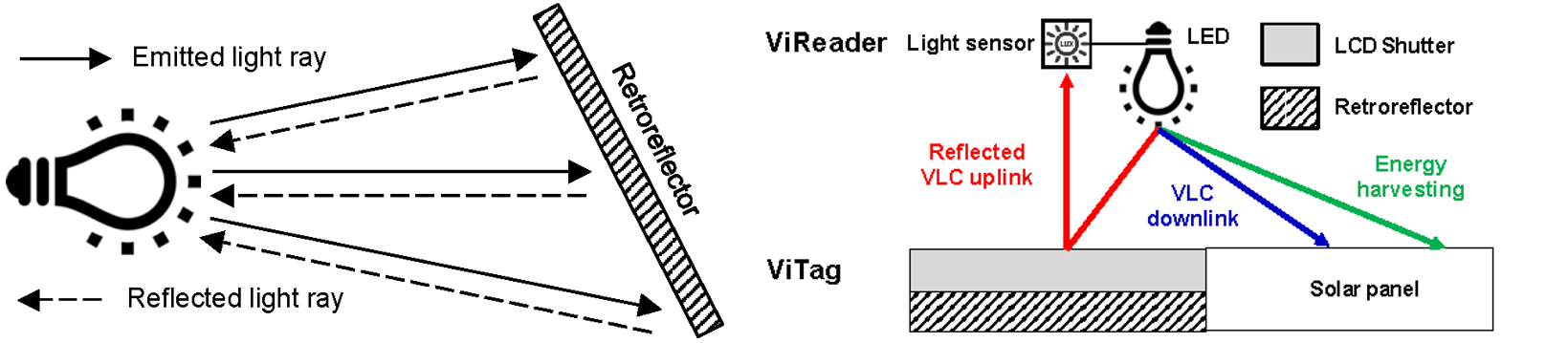
We introduce Visible Light IDentification (VLID), a novel ultra-low-power communication technology over visible light spectrum. In analogy to RFID, the basic operation of VLID is carried on an asymmetric optical link between readers with traditional visible light communication (VLC) frontend and tags with two ultra low power design treatments. First, it employs a retroreflector fabric and modulates the light (retro)reflection with a front LCD shutter - such a visible light backscatter design reduces more than three orders of power in uplink transmission than active VLC by avoiding signal generation; second, it multiplexes a single solar panel for simultaneous energy harvesting and communication - a key to realizing near-zero power downlink receiver. Our prototyped VLID system enables a Internet-of-Things (IoT) tag device to perform passive communication with the illuminating LEDs over the same light carrier and thus offers several favorable features including battery-free, sniff-proof, pointing-free and biologically friendly for human-centric use cases. We have been actively working on shipping this IoT connectivity technology to vehicular networking (V2X), augment reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) industry in a broader sense.
People
Students
| Xieyang Xu | Peking University |
| Yang Shen | Peking University |
| Junrui Yang | Stanford University |
| Guojun Chen | Peking University |
| Lilei Feng | Peking University |
| Purui Wang | Peking University |
| Yue Wu | Peking University |
| Tuochao Chen | Peking University |
| Kenuo Xu | Peking University |
Publications
[MobiCom'17] PassiveVLC: Enabling Practical Visible Light Backscatter Communication for Batery-free IoT Applications [PDF]
Xieyang Xu, Yang Shen, Junrui Yang, Chenren Xu, Guobin Shen, Guojun Chen, Yunzhe Ni